SqueakByExample:12.4: Difference between revisions
Onionmixer (talk | contribs) (pdf 원문에서 다음 페이지로 넘어가버린 이미지 추가) |
Onionmixer (talk | contribs) (용어수정) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==메타클래스 계층은 클래스 계층과 평행관계이다== | ||
Rule 7 에서는 메타클래스의 super클래스는 임의의 클래스가 될 수 없다고 하고 있습니다: 메타클래스의 super클래스는, 메타클래스의 고유인스턴스의 super클래스에 해당하는 메타클래스만 가능합니다<ref name="역자주1">TranslucentColor instance(metaclass) 의 superclass > Color 클래스의 instance 가 됩니다. 고로 이런 공식이 될 수 있겠습니다. metaclass(instance) superclass>originalclass(class)>superclass of originalclass(class)>metaclass of superclass of originalclass(instance). 결국 메타클래스의 superclass 는 원본이 되는 클래스의 상위클래스의 메타클래스가 된다는 얘깁니다. 메타클래스의 superclass 는 상위구현의 메타클래스만 된다는 의미가 되겠습니다.</ref>. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="smalltalk"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="smalltalk"> | ||
TranslucentColor class superclass ⇒ Color class | TranslucentColor class superclass ⇒ Color class | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
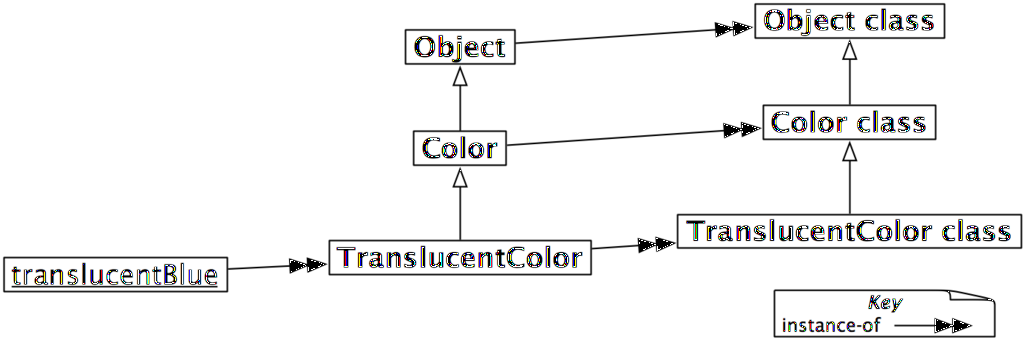
위의 결과가 바로 메타클래스의 계층은 클래스 계층과 평행구조를 이룬다는 의미이며, 그림 12.4 는 TranslucentColor 에 대한 계층이 어떻게 평생성을 가지는지를 보여줍니다: | |||
[[image:TranslucentMetaclassHierarchy.png|none|1024px|thumb|그림 12.4: 메타클래스 | [[image:TranslucentMetaclassHierarchy.png|none|1024px|thumb|그림 12.4: 메타클래스 계층은 클래스 계층과 평행관계를 이룬다.]] | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="smalltalk"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="smalltalk"> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
'''클래스와 | '''클래스와 객체의 일관성''' 잠시 쉬어가며 생각해보면, 객체 또는 클래스에 메시지를 보내는작업에서 양쪽의 차이가 없다는건 흥미로운 일입니다. 두 경우 모두, 사용할 메서드의 탐색은 수신자클래스부터 시작되서 상속관계를 쫒아갑니다. | ||
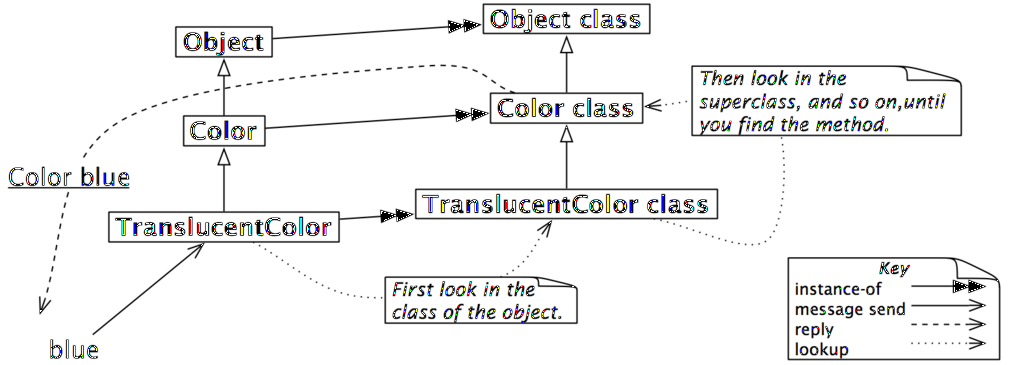
따라서 클래스에 보낸 메시지의 탐색은, 메타클래스의 상속계층을 쫒아가게 됩니다. 예를들어, blue 메서드는 Color 의 class side 에 정의되어 있습니다<ref name="역자주2">java 또는 c++ 에서는 static method 에 해당됩니다.</ref>. TranslucentColor 에 blue 라는 메시지를 전송하면 다른 메시지를 찾는것과 동일한 방식으로 메서드를 검색하게 됩니다. 즉 탐색은 TranslucentColor class 에서 일단 시작해서 대응되는 메서드를 발견할 때까지 메타클래스 계층을 따라 Color class 까지 더듬어 가게 됩니다(그림 12.5 참고)<ref name="역자주3">이건 좀 흥미롭습니다. class 의 definition 만 쫒아가는게 아니라 metaclass 의 상속계층을 쫒아가는게 기본이군요. 하긴 system browser 에서 확인되는게 metaclass 라면 당연한 결과같기는 합니다.</ref>. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="smalltalk"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="smalltalk"> | ||
TranslucentColor blue ⇒ Color blue | TranslucentColor blue ⇒ Color blue | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
TranslucentColor 의 인스턴스가 아니라, 일반적으로 Color blue 객체를 얻게된다는걸 주의해주시기 바랍니다-이상한부분은 어느곳에도 없습니다. 당연한 결과인거죠! | |||
[[image:TranslucentColorBlue.png|none|1024px|thumb|그림 12.5: 클래스를 위한 메시지 탐색은 일반 객체에 대해서도 동일합니다.]] | |||
위에서 확인한 바와같이, 스몰토크에서는 한결같은 방법으로 메서드 탐색을 하고 있다고 할 수 있습니다. 클래스도 단순히 객체이며, 모든 다른 객체도 동일하게 동작합니다. 클래스를 이용해서 새로운 인스턴스를 만드는것이 가능합니다만, 이런 동작은 클래스가 우현해 new 메시지에 반응할 수 있고, new 에 대한 메서드가 새 인스턴스 생성이 가능하기 때문인것 외에 다른 이유는 없습니다. 일반적으로 클래스 이외의 객체는 new 메시지에 응답할 수 없습니다만, 이렇게 new 메시지의 응답에 대한 동작제한을 한 이유는 new 메서드를 메타클래스 외에도 어디든 추가할 수 있게 되어버리기 때문이죠. | |||
클래스도 객체이기 때문에, inspect 가 가능합니다. | |||
{{CommentSqueak|Color blue 와 | {{CommentSqueak|Color blue 와 Color 를 inspect 하십시오.}} | ||
Color 의 인스턴스, 그리고 Color class 에 대한 조사를 할때는 주의해야합니다. 아마도 헷갈릴 수 있는데, inspector 의 제목표시줄은 inspect 의 대상이되는 객체의 클래스 이름을 표시하기 때문이죠. | |||
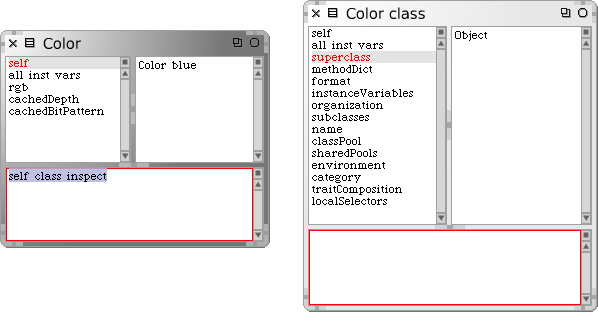
Color( | Color(객체 또는 인스턴스)의 Inspector 는 그림 12.6 에서 보이는것처럼, Color 클래스의 super클래스, 인스턴스변수, 메서드 Dictionary 등을 볼 수 있게 해줍니다. | ||
[[image:InspectingColor.png|none|598px|thumb|그림 12.6 클래스 또한 객체 입니다.]] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:18, 17 September 2013
메타클래스 계층은 클래스 계층과 평행관계이다
Rule 7 에서는 메타클래스의 super클래스는 임의의 클래스가 될 수 없다고 하고 있습니다: 메타클래스의 super클래스는, 메타클래스의 고유인스턴스의 super클래스에 해당하는 메타클래스만 가능합니다[1].
TranslucentColor class superclass ⇒ Color class
TranslucentColor superclass class ⇒ Color class
위의 결과가 바로 메타클래스의 계층은 클래스 계층과 평행구조를 이룬다는 의미이며, 그림 12.4 는 TranslucentColor 에 대한 계층이 어떻게 평생성을 가지는지를 보여줍니다:
TranslucentColor class ⇒ TranslucentColor class
TranslucentColor class superclass ⇒ Color class
TranslucentColor class superclass superclass ⇒ Object class
클래스와 객체의 일관성 잠시 쉬어가며 생각해보면, 객체 또는 클래스에 메시지를 보내는작업에서 양쪽의 차이가 없다는건 흥미로운 일입니다. 두 경우 모두, 사용할 메서드의 탐색은 수신자클래스부터 시작되서 상속관계를 쫒아갑니다.
따라서 클래스에 보낸 메시지의 탐색은, 메타클래스의 상속계층을 쫒아가게 됩니다. 예를들어, blue 메서드는 Color 의 class side 에 정의되어 있습니다[2]. TranslucentColor 에 blue 라는 메시지를 전송하면 다른 메시지를 찾는것과 동일한 방식으로 메서드를 검색하게 됩니다. 즉 탐색은 TranslucentColor class 에서 일단 시작해서 대응되는 메서드를 발견할 때까지 메타클래스 계층을 따라 Color class 까지 더듬어 가게 됩니다(그림 12.5 참고)[3].
TranslucentColor blue ⇒ Color blue
TranslucentColor 의 인스턴스가 아니라, 일반적으로 Color blue 객체를 얻게된다는걸 주의해주시기 바랍니다-이상한부분은 어느곳에도 없습니다. 당연한 결과인거죠!
위에서 확인한 바와같이, 스몰토크에서는 한결같은 방법으로 메서드 탐색을 하고 있다고 할 수 있습니다. 클래스도 단순히 객체이며, 모든 다른 객체도 동일하게 동작합니다. 클래스를 이용해서 새로운 인스턴스를 만드는것이 가능합니다만, 이런 동작은 클래스가 우현해 new 메시지에 반응할 수 있고, new 에 대한 메서드가 새 인스턴스 생성이 가능하기 때문인것 외에 다른 이유는 없습니다. 일반적으로 클래스 이외의 객체는 new 메시지에 응답할 수 없습니다만, 이렇게 new 메시지의 응답에 대한 동작제한을 한 이유는 new 메서드를 메타클래스 외에도 어디든 추가할 수 있게 되어버리기 때문이죠.
클래스도 객체이기 때문에, inspect 가 가능합니다.
![]() Color blue 와 Color 를 inspect 하십시오.
Color blue 와 Color 를 inspect 하십시오.
Color 의 인스턴스, 그리고 Color class 에 대한 조사를 할때는 주의해야합니다. 아마도 헷갈릴 수 있는데, inspector 의 제목표시줄은 inspect 의 대상이되는 객체의 클래스 이름을 표시하기 때문이죠.
Color(객체 또는 인스턴스)의 Inspector 는 그림 12.6 에서 보이는것처럼, Color 클래스의 super클래스, 인스턴스변수, 메서드 Dictionary 등을 볼 수 있게 해줍니다.
Notes
- ↑ TranslucentColor instance(metaclass) 의 superclass > Color 클래스의 instance 가 됩니다. 고로 이런 공식이 될 수 있겠습니다. metaclass(instance) superclass>originalclass(class)>superclass of originalclass(class)>metaclass of superclass of originalclass(instance). 결국 메타클래스의 superclass 는 원본이 되는 클래스의 상위클래스의 메타클래스가 된다는 얘깁니다. 메타클래스의 superclass 는 상위구현의 메타클래스만 된다는 의미가 되겠습니다.
- ↑ java 또는 c++ 에서는 static method 에 해당됩니다.
- ↑ 이건 좀 흥미롭습니다. class 의 definition 만 쫒아가는게 아니라 metaclass 의 상속계층을 쫒아가는게 기본이군요. 하긴 system browser 에서 확인되는게 metaclass 라면 당연한 결과같기는 합니다.