NeXTSTEPDRIVERKIT:Chapter2 5
- Threads in Kernel-Level Drivers
커널 수준 드라이버의 스레드(Threads in Kernel-Level Drivers)
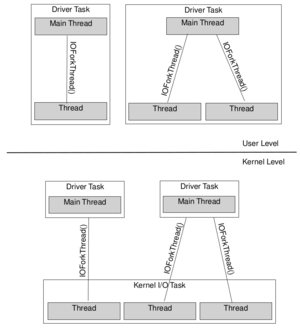
In a user-level driver, every thread the driver creates executes in the driver's own task, as shown in Figure 2-1. There's no way for any driver code to execute in any other task; neither the kernel nor any task besides the driver's own task ever executes the driver's code. Kernel-level drivers aren't so simple, however--and the Driver Kit currently supports only kernel-level drivers.
사용자 수준 드라이버에서 드라이버가 생성하는 모든 스레드는 그림 2-1 과 같이 드라이버 자체 태스크에서 실행됩니다.
드라이버 코드가 다른 태스크에서 실행될 수 있는 방법은 없습니다. 드라이버 자체의 태스크 외에 (그 어떤 외부의)커널이나 태스크도 드라이버 코드를 실행하지 않습니다. 커널 레벨 드라이버는 그렇게 간단하지 않지만, 현재의 Driver Kit 은 커널 레벨 드라이버만 지원합니다.
All kernel-level device drivers run in the kernel's memory address space, but unlike user-level drivers, their threads aren't all in the same task. A loaded kernel driver might run in a thread in the kernel task created especially for the driver. (A kernel task is a task that shares the kernel's address space but not the kernel's IPC space.) Additional threads created by kernel-level drivers execute as part of another kernel task, the kernel I/O task. Figure 2-1 shows the relationship between kernel-level driver threads and the kernel I/O task.
모든 커널 수준 장치 드라이버는 커널의 메모리 주소 공간에서 실행되지만, 사용자 수준 드라이버와는 다르게 해당 스레드가 모두 동일한 태스크에 존재하는것은 아닙니다. 로드 된 커널 드라이버는 특히 드라이버 용으로 작성된 커널 태스크의 스레드에서 실행될 수 있습니다. (커널 작업은 커널의 주소 공간을 공유하지만 커널의 IPC 공간은 공유하지 않는 작업) 커널 수준 드라이버에 의해 생성된 추가 스레드는 또다른 커널 작업의 일부인kernel I/O task 로 실행됩니다. 그림 2-1 에서는 커널 수준 드라이버 스레드와 커널 I/O 작업 간의 관계를 보여줍니다.
A complication for kernel-level drivers is that their code can execute in threads that don't belong to the driver. For example, the kernel invokes a network driver's outputPacket:address: method whenever the driver should transmit a packet. This method executes in whatever context the invoker of the method is in, not in the context of any of the driver's threads. Another example of executing in a nondriver thread is that drivers with UNIX entry points operate in the calling user process's context.
커널 수준 드라이버의 복잡성은 코드가 드라이버에 속하지 않는 스레드에서 실행될 수 있다는 것에서 비롯됩니다. 예를 들어, 커널은 드라이버가 패킷을 전송할 때마다 네트워크 드라이버의 outputPacket:address: 메소드를 호출합니다. 이 메서드는 드라이버의 스레드 컨텍스트가 아니라 메서드의 호출자가 있는 컨텍스트에서 실행됩니다. 비 드라이버 스레드(nondriver thread)에서 실행하는 또 다른 예제는 UNIX 진입 지점이있는 드라이버가 호출 사용자 프로세스의 컨텍스트에서 작동한다는 것입니다.
In general, if a method or function isn't always called directly by an I/O thread (or by functions or methods that are called directly by the I/O thread) and the documentation doesn't say that the method is called in the context of the kernel I/O task, you should assume that the method or function has been called by an unknown thread in an unknown task.
일반적으로 메서드 또는 함수가 I/O 스레드 (또는 I/O 스레드에 의해 직접 호출되는 함수 또는 메서드)에 의해 직접 호출되는 것은 아니며, 문서에서 해당 메서드가 호출되었다고 하지는 않으며, 커널 입출력 태스크의 컨텍스트에서 알 수 없는 태스크의 알 수 없는 스레드가 메소드 또는 함수를 호출했다고 가정해야 합니다.